APPENDIX 4
USES OR FEATURES
INTRODUCTION
Blockchain is one of the eight enabling technologies that will facilitate the creation of the Metaverse (Lik-Hang Lee). Many components of Web 3.0 and the Metaverse rely on blockchain technology, which is rather recent in development. Blockchain is not synonymous with cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, or NFTs, but it is the foundation upon which they are built.
Blockchain is also known as a “hyperledger” (Lik-Hang Lee) or distributed ledger technology (DLT) (Binance). A blockchain has unique properties and there are rules about how data can be added, and once the data has been stored, it’s virtually impossible to modify or delete it. Data is added over time as blocks. Each block points to the previous block through its hash – it’s traceable and easy to see if modified. Hashing is the glue that holds blocks together. It consists of taking data of any size and passing it through a mathematical function to produce an output (a hash) that’s always the same length.
- Hashes make it “astronomically low” to find the same hash twice. Rarely this happens in a “collision” (Binance).
- Hashing can’t easily be reverted (hacked) except through brute force of guessing inputs.
- Although not all hash functions involve the use of cryptography, the so-called cryptographic hash functions are at the core of cryptocurrencies. Thanks to them, blockchains and other distributed systems are able to achieve significant levels of data integrity and security. (Binance)
USES OR FEATURES
- Interoperability: Blockchain technology is continuously improving compatibility between different platforms. Projects like Polkadot (DOT) and Avalanche (AVAX) allow for creating custom blockchains that can interact with each other. A single metaverse will need to connect multiple projects, and blockchain technology already has solutions for this. Three examples of early versions of the metaverse; SecondLife, Axie Infinity, Decentraland. (Binance)
- Decentralized: “You could argue that the ledger is simultaneously owned by everyone: participants reach an agreement on what it looks like at any given moment.” (Binance)
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are chunks of code that, like NFTs, also live on a blockchain. These contracts are publicly-visible, immutable chunks of code that can manage cryptocurrency in a completely transparent and decentralized way. This means with a purchase, the contract can route the cryptocurrency in a certain unchangeable way to a specific wallet, and the currency can be tracked. “Smart contracts like this mean that you no longer have to trust the creators of a project to stand by their claims. Instead, you can simply review the code which will always do exactly what it’s programmed to. Code is law!” (FunkyMonkeys).
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): NFTs are hosted on blockchain technology. NFTs are “unique, digital items with blockchain-managed ownership. Examples include collectibles, game items, digital art, event tickets, domain names, and even ownership records for physical assets.” They just vary in their tradeability, liquidity, and interoperability. Blockchains provide a coordination layer for digital assets, giving users ownership and management permission. (Open Sea)
- Cryptocurrency: Is based on cryptographic hashes in blockchain. There are various cryptocurrencies held in crypto wallets. “Bitcoin’s strength lies in how it approaches trust. Instead of checking the trustworthiness of each party, the system assumes that everyone behaves selfishly. No matter how greedily traders act, the blockchain retains integrity and can be trusted even if the parties cannot.” Cryptocurrency’s foundation on blockchain is purported to provide security and transparency. (Nature)
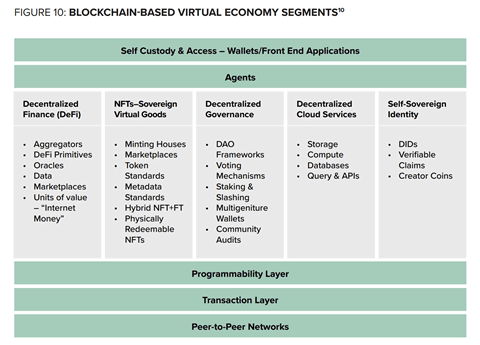
RISKS AND MITIGANTS
“When information is money, data security, transparency and accountability are crucial.” (Nature)
Because of the decentralized nature of blockchain, it can be difficult to recover stolen virtual goods or currency. One virtual art collector had $2.2 million in NFTs stolen, and ultimately no regulatory authority could help him restore it. Only Open Sea themselves (the broker) was able to help (Tran).
Blockchain is one-way encryption – almost impossible to find the origin of the block to reverse the transaction. However, within ten years, quantum computers may be able to calculate the one-way functions, including blockchains, that are used to secure the Internet and financial transactions. Widely deployed one-way encryption will instantly become obsolete. Quantum computers “are currently much less powerful than conventional computers, but will soon be able to outperform them on certain tasks”. Blockchain at risk because it only has one line of defense. Other items have MFA lines of defense, such as security questions, identity checks, even the human element of a cashier determining if the identity of the buyer matches.” “If nothing is done to update the protocols, cryptocurrencies will crash once quantum computers become available.” (Nature) To mitigate (Nature):
- Use quantum computers to create quantum cryptography, though the barrier to this is high infrastructure cost and requirements.
- Develop alternative encryption functions in the meanwhile.
- Develop a quantum internet “connecting quantum computers across a quantum communications network”. Timeframe: several decades away.
- The longer-term answer is to develop and scale up the quantum communication network and, subsequently, the quantum internet. This will take major investments from governments. However, countries will benefit from the greater security offered. Early adopters are those conducting research already.
- To attract venture capitalists, the winning quantum products should have business models that require few assets, are low on manufacturing costs and clearly help customers to increase their revenues. Through the cloud, a company could benefit from using existing data centers when applying classical solvers to simple problems, and invoke quantum processors when it matters. (Nature)
FUTURE OUTLOOK
Blockchain looks to be a key technology to the advancement of many of the enabling technologies of Web 3.0 and the Metaverse. Many different sectors have already invested in blockchain technology (read more here) and will continue to build upon this technology for their vertical markets. When investing in blockchain-enabled technologies, despite it being characterized as secure and decentralized, keep an eye on the risks and mitigating factors. Here are some forecasts and thoughts from various sources:
- CBI has already made several investments and is currently developing AlphaVerse, a blockchain technology-based virtual world or metaverse that will be opening in summer 2022. Yahoo Finance
- “By 2025, up to 10% of global gross domestic product is likely to be stored on blockchains.” (Nature)
- “The real magic lies in understanding how blockchain technology itself unlocks exponential disruptive growth for new players who’ll eat some part or the whole of established category players. And even if they secure only 10% of multibillion-dollar industries, they’ll be exceptionally lucrative.” (Daily Maverick)
- “As standalone data structures, blockchains are only really useful in niche applications. Where things get interesting is when we use them as tools for strangers to coordinate amongst themselves. Combined with other technologies and some game theory, a blockchain can act as a distributed ledger that’s controlled by no one.” (Binance)
- “Blockchain domains have two key use cases; turning hexadecimal wallet addresses into human-readable names and enabling censorship-resistant websites. As a result, trading crypto domains is big business for speculators, NFT traders, and metaverse natives alike.” (Open Sea)
- “Virtual worlds are blockchain-fueled alternative realities where users can create and trade digital goods, play games, and display NFTs in galleries, among other intriguing use cases. Non-fungible token categories like art, collectibles, and domain names are all put to use in the metaverse, with ecosystems built and maintained by the crypto community.” (Open Sea)
FURTHER READING AND SOURCES
- Binance Academy, February 2022. ‘What is Blockchain technology? The Ultimate Guide.’ Available at: https://academy.binance.com/en/articles/what-is-blockchain-technology-a-comprehensive-guide-for-beginners. Accessed February 2022.
- Binance Academy, July 2019. ‘What is Hashing?’ Available at: https://academy.binance.com/en/articles/what-is-hashing. Accessed March 2022.
- Aleksey Fedorov, November 2018. ‘Quantum Computers put Blockchain Security at Risk.’ Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-018-07449-z. Accessed March 2022
- Masoud Mohseni, March 2017. ‘Commercialize Quantum Technologies in Five Years.’ Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/543171a. Accessed March 2022.
- Marco Schletz, August 2021. ‘Blockchain Energy Consumption.’ Available at: http://datadrivenlab.org/climate/blockchain-energy-consumption-debunking-the-misperceptions-of-bitcoins-and-blockchains-climate-impact/. Accessed March 2022.
- Gwyneth Iredale, November 24, 2021. 6 Key Blockchain Features You Need To Know Now. Available at: https://101blockchains.com/introduction-to-blockchain-features/. Accessed March 2022.
- Diego Geroni, March 13, 2021. Top 20 Promising Blockchain Projects In 2021. Available at: https://101blockchains.com/top-blockchain-projects-ideas/. Accessed March 2022.
- Gwyneth Iredale, December 26, 2020. Top 50 Companies that Has Adopted Blockchain Technology. Available at: https://101blockchains.com/companies-using-blockchain-technology/. Accessed March 2022.
- Available at https://funkymonkeys.io/. Accessed March 2022.
- Open Sea. ‘Discover, collect, and sell extraordinary NFTs’. Available at https://opensea.io/ Accessed March 2022.
- Devin Finzer, January 2020. ‘The Non-Fungible Token Bible.’ Available at: https://opensea.io/blog/guides/non-fungible-tokens/. Accessed March 2022.
- Russell Brandom, February 2022. ‘$1.7 million in NFTs stolen in apparent phishing attack on OpenSea users.’ Available at: https://www.theverge.com/2022/2/20/22943228/opensea-phishing-hack-smart-contract-bug-stolen-nft. Accessed March 2022.
- Tony Tran, January 2022. ‘HACKERS STEAL $2.2 MILLION WORTH OF NFTS FROM ART COLLECTOR.’ Available: https://futurism.com/the-byte/hackers-steal-nfts-art-collector. Accessed March 2022.
- Guillaume Chapron, May 2017. ‘The Environment needs Cryptogovernance.’ Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/545403a. Accessed March 2022.
